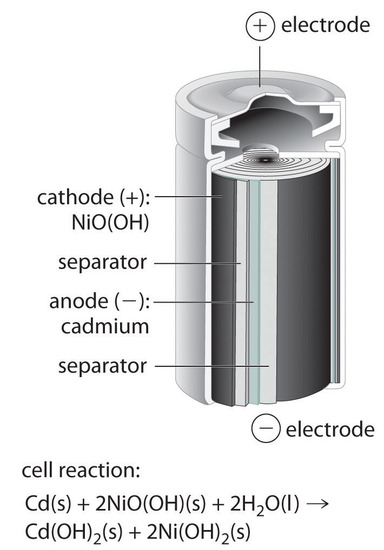
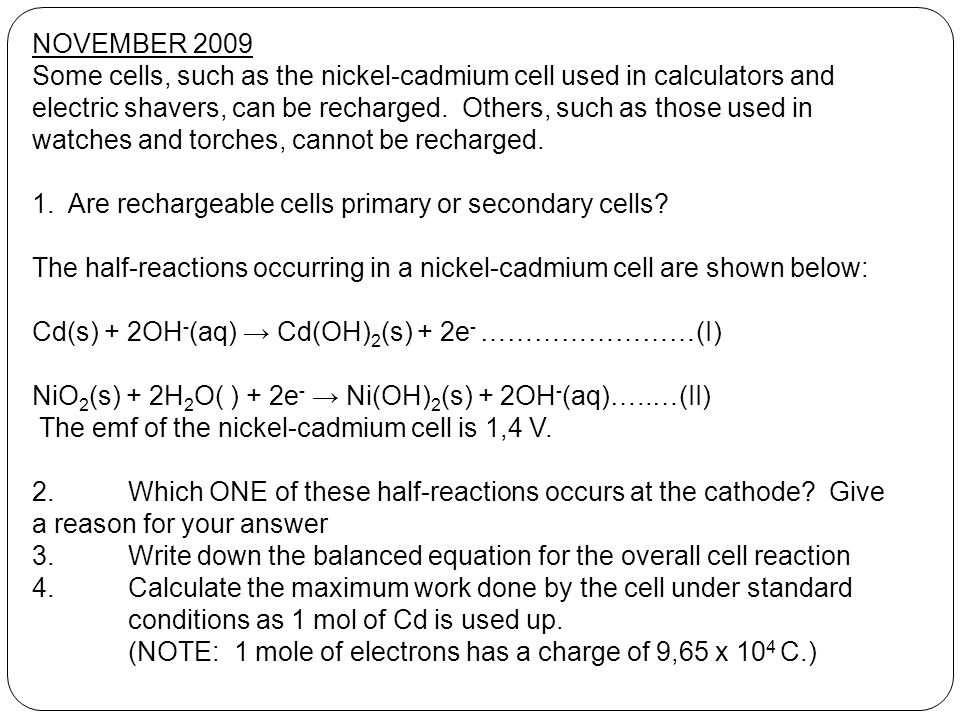
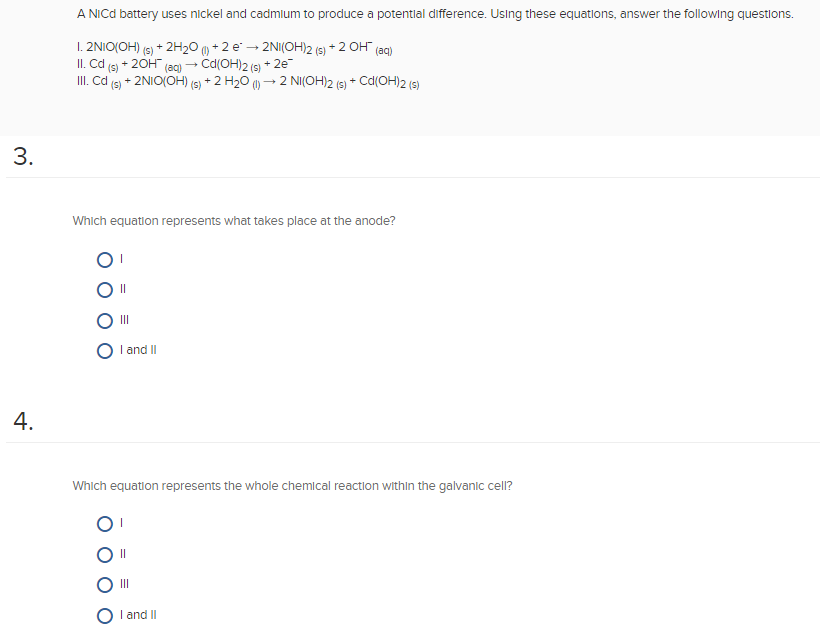
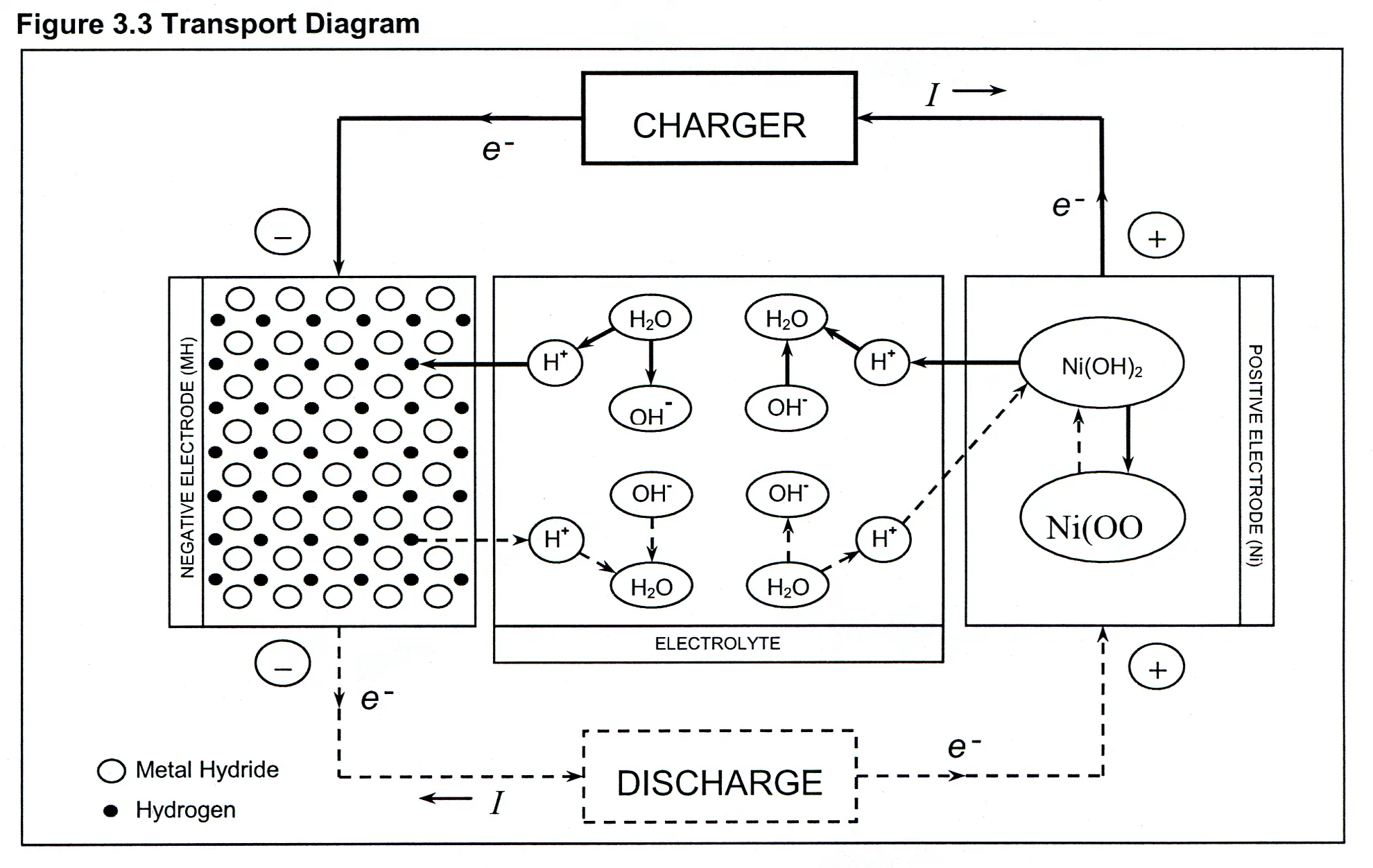
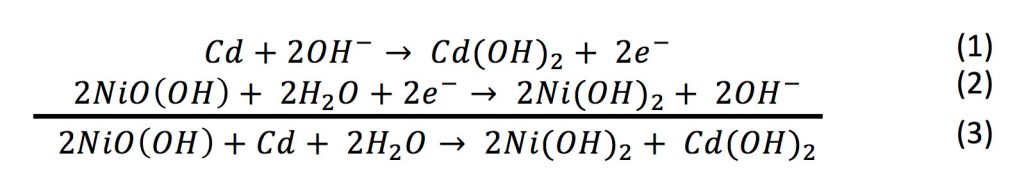The nickel cadmium battery ni cd battery or nicad battery is a type of rechargeable battery using nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes.
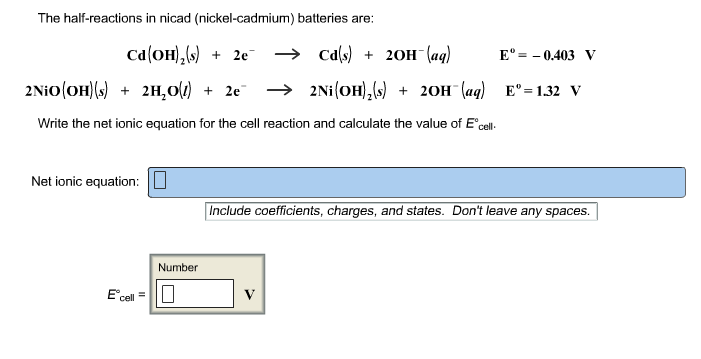
Nickel cadmium battery reaction equation.
The electrolyte is a solution of potassium hydroxide koh with a small addition of lithium hydrate which increases the capacity and life of the battery.
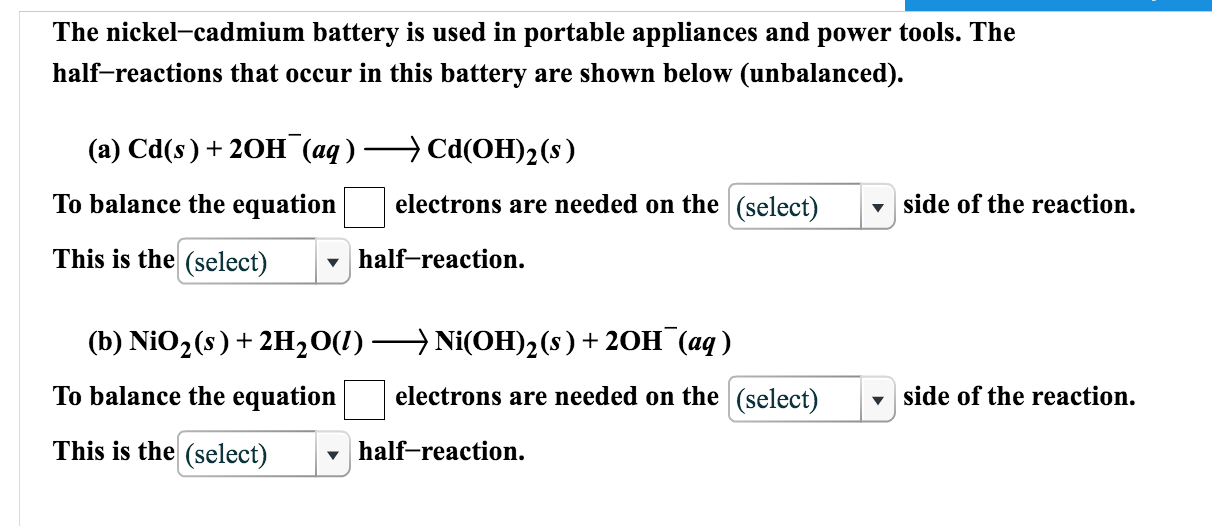
In the case of the nickel cadmium battery the cadmium electrode has two important features.
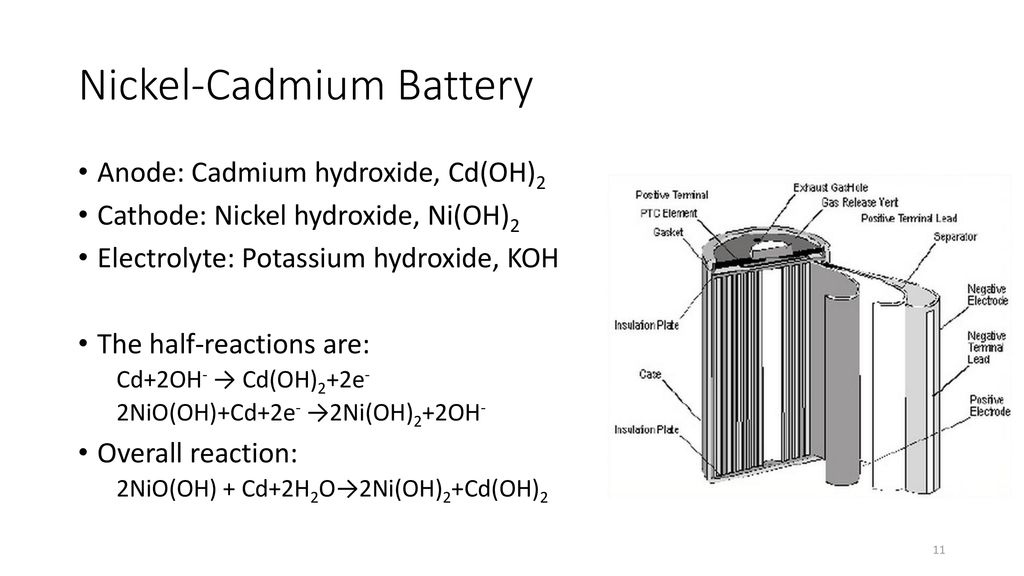
The nickel cadmium battery system still uses the same positive electrode as the nickel iron one while the negative electrode is cadmium.
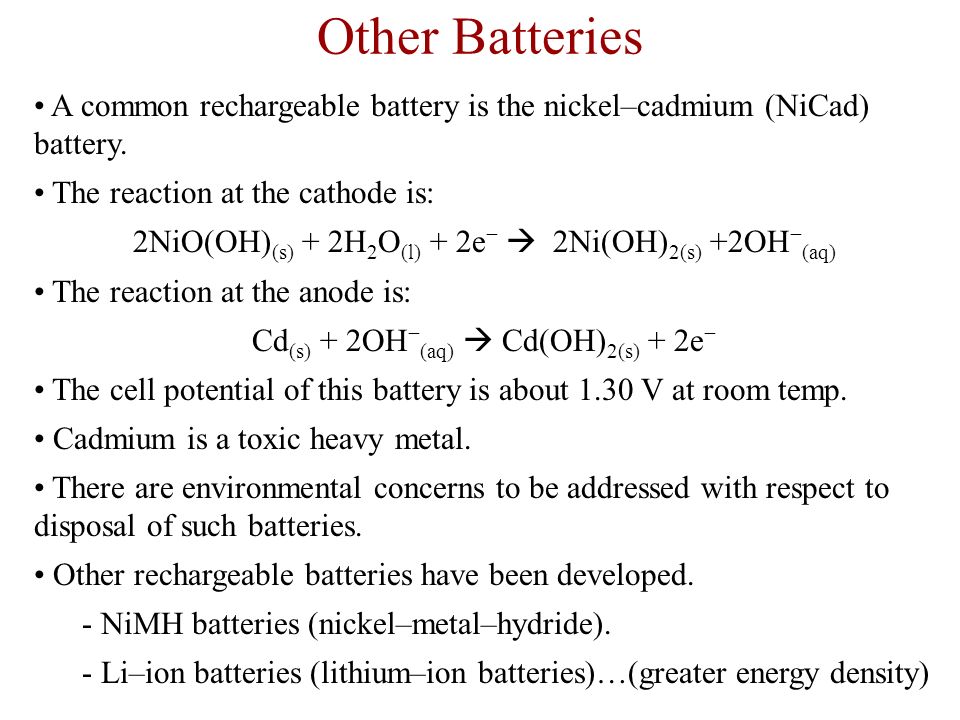
The reactions at the nickel oxide electrode are.
The maximum cell voltage during charge is 1 3 v and the average cell voltage is 1 2 v.
First the rate of hydrogen formation on cadmium is very slow compared with that on pure zinc or pure.
The abbreviation ni cd is derived from the chemical symbols of nickel.
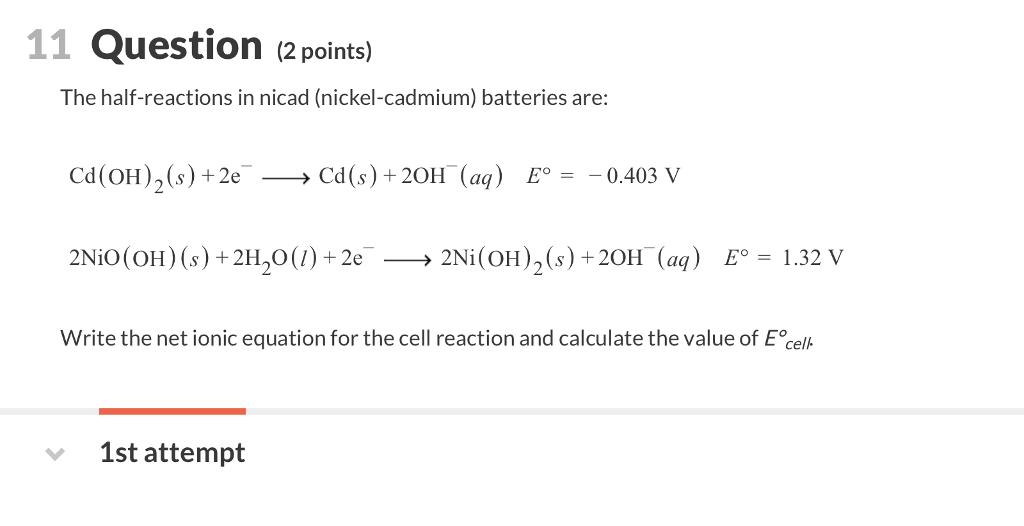
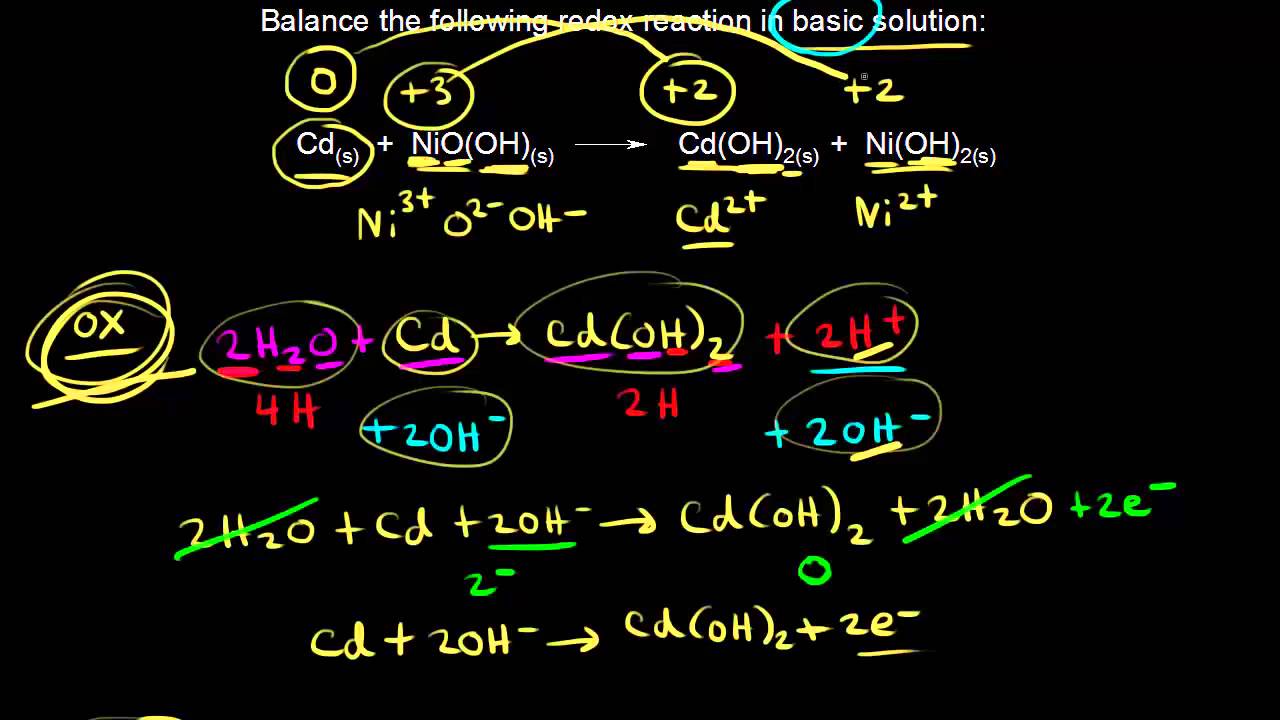
And our two products cadmium hydroxide and nickel hydroxide are both solids that precipitate on the electrodes in the battery and that makes it easy to reverse the reaction because if you re reversing your reaction you need to start with cadmium hydroxide and nickel hydroxide and those are already there so it s easy to reverse this.
The chemical conversion is reverted when a discharged battery is charged again.
Nickel cadmium batteries are used in various developmental electric vehicles.
Nickel cadmium batteries at the 1 2h rate yield twice the energy density of lead acid batteries i e.
In eqns 4 6 the cell reactions during charging and discharging are presented.
They operate over a wide temperature range give approximately 2000 cycles and can be charged in less than 1 h.
The active material of the positive plate anode is ni oh 4 and the negative plate cathode is of cadmium cd when fully charged.
Nickel cadmium battery contributors and attributions rechargeable batteries also known as secondary cells are batteries that potentially consist of reversible cell reactions that allow them to recharge or regain their cell potential through the work done by passing currents of electricity.